- May 15, 2023
- Posted by: Harish Gopi
- Category: Digital Assurance

Introduction
Quality Assurance is essential for ensuring that digital products, including websites, apps, and software, are usable by all users, including those with disabilities. Testing for accessibility enables the detection of any obstacles that could prevent individuals with disabilities from using digital products. This article’s goal is to give a general overview of accessibility testing and explain why it’s crucial for producing accessible digital products
1. What is accessibility testing?
The process of assessing a digital product’s usability by those with impairments is known as accessibility testing. It involves examining a product’s usability and user interface using assistive technology like voice recognition software, keyboard-only navigation, and screen readers. A product’s compliance with accessibility standards like the Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG), and the Americans with Disabilities Act is also evaluated during accessibility testing ( ADA).
1.1. Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG)
Here are the Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) according to the checkpoints and priority levels:
Level A
Describes the components of a web page that must be usable by people with physical disabilities for them to access the content at all.
Level AA
Contains elements on web pages that must be readable for a group of users to access the content.
Level AAA
Outlines web page components that can be made accessible so that the site can be used by the greatest number of people with disabilities.
1.2. Principles of WCAG
Here are a few common scenarios to validate the Data part:
Perceivable
All users, including those with disabilities, must be able to easily perceive and comprehend the content as it is presented. The provision of non-text content substitutes, such as pictures, videos, and audio, falls under this category.
Operable
The interface and navigation of the website must be operable for all users, including those who use assistive technologies such as screen readers or voice recognition software. This includes providing keyboard accessibility, clear and consistent navigation, and allowing enough time for users to interact with content.
Understandable
The content and interface must be presented in a way that is easy to understand for all users, including those with cognitive disabilities or who may have difficulty with language or reading. This includes using clear and simple language, providing context and structure, and avoiding jargon and overly complex terminology.
Robust
The content must be robust enough to work with a variety of user agents, including assistive technologies, and future technologies that may be developed. This includes using accessible markup and code, following standards and guidelines.
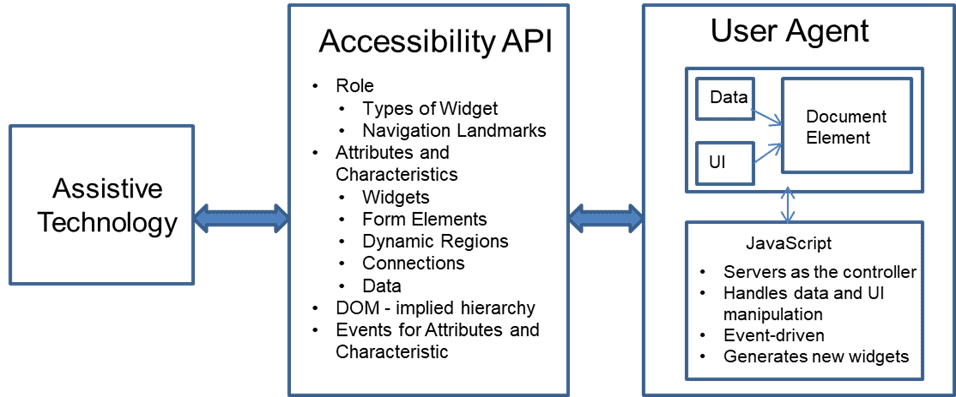
1.3. Assistive Technology
Assistive technology is a type of technology that is designed to assist people with disabilities in performing tasks that may be difficult or impossible without assistance. These technologies are designed to enhance accessibility, mobility, communication, and independence for people with physical disabilities.
Here are some examples of assistive technology:
Screen readers: These are software programs that can read text on a computer screen aloud for users who are visually impaired.
Wheelchairs: These are devices that enable people with mobility impairments to move around more easily.
Hearing aids: These are devices that amplify sound for people who are hard of hearing.
Braille displays: These are devices that convert digital text into Braille for users who are blind.
Voice recognition software: This technology allows users to control their computer or mobile device using their voice.
Rosthetic limbs: These are devices that replace missing or amputated limbs and help users do their everyday tasks.
Augmentative and alternative communication (AAC) devices: These are devices that help people who have difficulty speaking to communicate using alternative methods, such as sign language, or text-to-speech software.
Electronic magnifiers: These are devices that magnify text or images for users with low vision.
Environmental control systems: These are devices that allow users to control appliances, lights, and other household items using their voice or other assistive technology.
Assistive listening devices: These are devices that help people with hearing impairments hear more clearly in specific environments, such as classrooms or theaters.
By giving people with physical disabilities more independence, access to information, and chances to actively participate in their quality of life
Also Read this interesting blog on Testing the Reality of Apps in Physical devices
2. Importance of Accessibility testing
The use of digital products by everyone, including those with disabilities, is ensured by accessibility testing. Digital products may not be accessible to users with disabilities if they undergone accessibility testing. For instance, a non-accessible website may not be usable with a screen reader, making it impossible for people who are blind to use the site. Additionally, visitors who are color blind may find it difficult to understand the text on the page if a non-accessible website lacks sufficient color contrast.
Another reason accessibility testing is crucial is that it can assist businesses in adhering to accessibility laws and regulations. According to the Americans with Disabilities Act ( ADA), businesses must offer people with disabilities equal access to their products and services. Like this, government agencies must comply with Section 508 of the Rehabilitation Act, which directs that their electronic and information technologies be accessible to people with physical disabilities. Organizations may be able to stay out of court and other legal problems by following these regulations.
3. Testing Approach
Accessibility testing can be performed manually or with the use of automated tools. Manual testing involves using assistive technologies such as screen readers, keyboard-only navigation, and voice recognition software to evaluate a product’s accessibility. Manual testing is time-consuming and requires a high level of expertise to identify accessibility issues.
Automation testing involves using tools that scan a product’s code and user interface to identify accessibility issues. Automated testing is faster than manual testing and can identify many accessibility issues quickly. However, automated testing has its limitations, as it cannot identify all accessibility issues, especially those related to user experience. In general, a combination of manual and automated testing is recommended to ensure that a digital product is fully accessible.
3.1. Accessibility Testing Tools
Accessibility testing tools are software programs that can help developers and testers ensure that their applications or websites are accessible to all users, including those with certain disabilities.
Here are some popular accessibility testing tools:
| S.No | Tools | Functionality |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | WAVE | A free browser extension that provides feedback on the accessibility of web content. |
| 2 | Axe | An accessibility testing tool that can be used as a browser extension or as a command-line tool. |
| 3 | aXe Coconut | A cloud-based accessibility testing tool that provides comprehensive reports on the accessibility of web content. |
| 4 | Accessibility Insights | A suite of tools for testing the accessibility of web content, including a browser extension and a command-line tool. |
| 5 | Color Contrast Analyzer | A tool that allows developers to check the color contrast of web content to ensure it is accessible for users with visual impairments. |
| 6 | NVDA | A free screen reader for Windows that can be used to test the accessibility of web content. |
| 7 | VoiceOver | A built-in screen reader for Mac that can be used to test the accessibility of web content. |
| 8 | JAWS | A commercial screen reader for Windows that can be used to test the accessibility of web content. |
| 9 | Chrome DevTools | A built-in browser tool that can be used to test the accessibility of web content. |
| 10 | Tenon | A cloud-based accessibility testing tool that provides detailed reports on the accessibility of web content. |
These are just a few of the many accessibility testing tools available. It’s important to choose the right tool for your needs and to regularly test your website or application for accessibility to ensure that all users can access your content.
Ensure your website or application is accessible to all. Contact us to schedule your ADA compliance testing today.
Click here
Conclusion
Accessibility testing is a critical process that ensures websites and digital platforms are accessible to individuals with disabilities. It is essential to comply with the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) to provide equal opportunities for everyone to access information and services online. Testing for ADA compliance helps to identify and fix accessibility barriers, ensuring that individuals with physical disabilities can use the digital platforms without encountering any difficulties. Furthermore, it enhances the user experience and improves the reputation of the organization. By conducting regular ADA compliance testing, organizations can ensure that their digital platforms are accessible to all, regardless of their disabilities.
